ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
1 Domeniu de aplicareAcest STANDARD specifică cerințele tehnice și metodele de testare pentru galvanizarea aliajelor de staniu-plumb cu conținut de staniu variind de la 50% la 70%(raportul de masă) (vedea 10.3).
Acest STANDARD SE APLICĂ la tablă – galvanizare din aliaj de plumb pentru prevenirea coroziunii și îmbunătățirea performanței de sudare a produselor electronice și electrice și a altor produse metalice.
Acest standard este de asemenea aplicabil acoperirilor din aliaj de staniu-plumb din alte compoziții, dar trebuie remarcat faptul că proprietățile acestor acoperiri pot diferi de cele ale acoperirilor din aliaj de staniu-plumb în intervalul de compoziție de aliaj de mai sus.
Metoda de clasificare din acest standard indică în mod clar categoria metalului de bază și compoziția acoperirii cu un anumit interval de conținut de staniu, precum și prevederile stratului de topire la cald și stratului de depunere strălucitoare.
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
Acest standard nu se aplică:
A) acoperire din aliaj de staniu-plumb pe piesele filetate;
b) acoperire din aliaj de staniu-plumb pe rulmenți;
Acoperire din aliaj de staniu-plumb pe foi neprelucrate, benzi sau fire sau pe piese formate din acestea;
d) Acoperire din aliaj de staniu-plumb pe oțel cu rezistență la tracțiune mai mare de 1000Mpa(sau duritatea corespunzătoare), ca atare oțel este predispus la fragilitatea hidrogenului după galvanizare (vedea 8.2).
2 Standarde de referință
Următoarele standarde conțin prevederi care, prin referire în acest standard, constituie prevederi ale acestui standard. La momentul publicării acestui standard, toate versiunile prezentate sunt valide. Toate standardele sunt supuse revizuirii, iar părțile care utilizează acest standard ar trebui să exploreze posibilitatea de a utiliza versiuni noi ale următoarelor standarde.
Proceduri de bază de testare a mediului pentru produse electronice și electrice Test T: Metoda de testare a lipirii (echiv]EC68-2-20:1979)
Măsurarea grosimii stratului de acoperire metalică Metoda Coulomb cu anod dizolvat (idtIs02177:1985)
Metoda de testare a rezistenței de aderență a acoperirilor metalice (electrodepus și depus chimic) pe substraturi metalice (eqvIS02819:1980)
Produse industriale ușoare - metodă de testare pentru grosimea acoperirilor metalice și a acoperirilor tratate chimic — metoda de retrodifuzare a razei β (idtIS03543:1981)
Metode de măsurare microscopică a grosimii secțiunii transversale a acoperirilor de metal și oxid (eqvIS01463:1982)
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
Test de coroziune cu dioxid de sulf pentru metale și alte învelișuri neorganice în condiții normale de condensare (eqvIS06988:1985)
Test de coroziune în atmosferă artificială Test de pulverizare cu sare (eqvIS09227:1990)
Metode de analiză chimică a lipiturii staniu-plumb – Determinarea conținutului de staniu prin analiza cu iodat
Definiții și reguli generale pentru măsurarea grosimii metalelor și a altor acoperiri anorganice (eqvIS020 “:1990)
Proceduri pentru inspecția prin eșantionare a capacelor metalice electrodepuse și a numărului de finisare aferente (eqvIs04519:1980)
Măsurarea grosimii capacului metalic Spectrometrie cu raze X (eqvIS03497:1990)
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
3 Definiții
Următoarele definiții sunt utilizate în acest standard.
3.1 Suprafața principală suprafață semnificativă
O anumită suprafață pe piesa de prelucrat care a fost sau urmează să fie placată, pe care acoperirea este importantă pentru aspectul și/sau performanța piesei de prelucrat și trebuie să îndeplinească toate cerințele specificate în standard.
3.2 Suprafața de măsurare de bază se referă la zona de început
O zonă a suprafeței principale în care sunt necesare un număr specificat de măsurători individuale.
3.3 Topitură la cald fl0w-topire
Un proces UTILIZAT prin placarea topită PENTRU a îmbunătăți CALITATEA suprafeței pentru a obține proprietățile dorite, cum ar fi luminozitatea sau proprietățile de lipire (vezi D4 în Anexa D(O ANEXĂ SUGERATĂ)).
Information TO BE PROVIDED BY THE DEMANDER TO THE ELECTROPLATING MANUFACTURER
4.1 Necessary Information
The Demander shall provide the following information to the electroplating manufacturer:
A) This national standard No.
b) properties of the matrix metal (vezi capitolul 5);
c) Condition number (vedea 7.1) or coating classification number (vedea 7.2) and alloy composition requirements (vedea 10.3); d) Whether the composition of the coating should be tested (vedea 10.3);
d) Specify the main surface of the workpiece to be plated, if marked with drawings or provided with suitably marked samples;
f) Sampling and inspection requirements (vezi capitolul 6);
g) Unavoidable joint corner traces and other acceptable coating defects on the workpiece (vedea 10.1);
h) the bonding strength test method used (vedea 10.4);
i) Special post-plating treatment (see D3.1 in Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
4.2 Supplementary Information
The Demander may also request the following supplementary information:
A) cerințele pentru tratamentul termic (vezi capitolul 8);
b) Cerințe pentru testarea porozității (vedea 10.5);
Cerințe de testare a lipirii și metode de încercare și condiții de utilizare (vedea 10.6);
d) Cerințe speciale pentru acoperirile inferioare (vezi capitolul 9);
) mostre care indică cerințele de aspect ale acoperirii (vezi 10.l);
f) cerințe speciale de pretratare;
g) Cerințe speciale de ambalare pentru piesele autoplacate.
Notă: Solicitantul va furniza conținutul specificat în 4.1 și, daca este necesar, 4.2. Nu este suficient să se furnizeze numărul acestui standard fără acest conținut.
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
5 Matrice
Acest standard nu necesită starea suprafeței, aspectul sau rugozitatea suprafeței substratului înainte de placare (vezi D2.1 din Anexa D). Dar deoarece calitatea suprafeței substratului este prea slabă pentru a face acoperirea nu poate îndeplini cerințele de aspect și/sau performanță, nu poate fi considerată calitatea producției de placare nu îndeplinește cerințele.
6 Take samples
When it is necessary to check whether the tIN-lead coating meets the requirements specified in Chapter 10 of this standard, sampling shall be carried out according to the sampling method specified in GB/T12,609, and the acceptance level shall be agreed between the supply and demand parties.
7 Classification
7.1 Use condition number
According to the following conditions of use environment and use condition number to indicate the severity of use conditions:
4 Particularly harsh as used outdoors under harsh corrosive conditions (see D1 in Appendix D);
3 Harsh as typical outdoor temperature conditions;
2 Medium as used for indoor slightly condensation conditions;
Mild AS USED in indoor dry atmosphere conditions, where welding performance is the main requirement. note
1 See 10.2, where guidelines on the relationship between the use of condition numbers and minimum thickness are given.
When THE use condition number or data layer classification number is specified, attention should be paid to the tin _ lead alloy in the ring with abrasives or in some organic volatile vapors
Easily damaged in the environment (see Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
7.2 Coating classification number
The coating grade number is composed of four parts, among which the first two parts shall be separated by a short slash line. Such as fbcd
Unde :a represents the chemical symbol of the matrix metal (or the main component in the alloy matrix);
b represents the chemical symbol of the bottom coating metal (or the main component of the alloy bottom coating), and then the minimum thickness of the bottom coating is represented by a number, in µm, which can be omitted if there is no bottom coating (see 4.2d));
One represents the composition of the coating, the method is the chemical symbol sn and then represents the mass percentage of tin in the coating, and then a short horizontal line and chemical symbol pb, and then the minimum thickness of tin _ lead coating, unit µm;
d 1 represents the finishing state of the coating surface, symbol m is no light coating,b is bright coating,f is hot melt coating.
De exemplu :Fe/Ni5Sn60-Pb10f the classification number indicates that the base metal is iron and steel, the bottom coating is nickel coating at least 5µm thick, the nominal tin content of tin _ lead coating is 60%(raportul de masă), at least 10µm thick, and has been hot melt treated.
Heat TREATMENT OF steel
8.1 Stress relief before plating
The deep cold deformation work hardened steel parts should be heat-treated at 190~220℃ for 1h before electroplating. To relieve stress.
After carburizing, flame quenching or high frequency induction quenching and subsequent grinding of some steel, with the above conditions will damage its performance, can be replaced by a lower temperature to eliminate stress, such as 130~150℃, the treatment time is not less than 5h.
8.2 Elimination of hydrogen embritculation after plating
Because the diffusion of hydrogen through the tin-lead coating is very slow, and the coating will melt at the temperature required by the hydrogen removal treatment, the heat treatment to eliminate hydrogen embrittlement is not announced after electroplating.
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
Requirements for the bottom coating
For any of the following reasons, it is necessary to electroplate the bottom coating for some matrix materials:
A) Prevention of diffusion (see D2.2 and D2.3 in Appendix D);
b) Maintain welding performance (see D2.2, D2.3 and D2.4 in Appendix D);
c) Guarantee bond strength (see D2.4 and D2.5 in Appendix D);
d) Improve and f erodibility.
When choosing the bottom coating or the bottom coating system, it should be noted that it should not bring bad performance, such as hydrogen embrittance of the base material or the plated parts, and the use of high stress nickel should be avoided.
If the substrate material is a zinc-containing copper alloy and weldability is required, in addition to the specified tin-lead alloy coating thickness (vedea 10.2), a nickel or copper substrate of a minimum local thickness of 2.5µm is required to maintain good appearance and bond strength (see D2.3 in Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
If a bottom coating is specified, its performance (see Appendix D) and minimum local thickness (vedea 10.2) shall be specified by the Demander.
The thickness of a single or multiple substrate coating shall be measured using the appropriate method specified in Appendix B(Appendix to the standard).
10 Requirements for coating
10.1 Appearance
During visual inspection, there should be no visible defects on the main surface of the plated parts, such as foaming, găuri, roughness, cracks or local no coating, and there should be no stains or discoloration.
The Demander shall specify acceptable and unavoidable parts of joint corners and allowable defects on non-primary surfaces.
After electroplating, the surface of the workpiece should be clean, no damage, uniform, no nodules, and there should be no non-hole wet zone at the melting place. The reticulate pattern that may appear on the surface cannot be regarded as unqualified.
If necessary, samples indicating the appearance requirements of the coating shall be provided or approved by the demander.
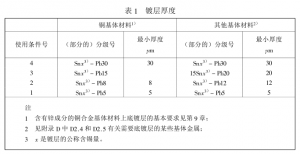
10.2 Grosime
The TIN-LEAD COATINGS ARE CLASSIFIED BY THICKNESS AND THE MINIMUM thickness value FOR EACH CONDITION NUMBER (SEE 7.1) IS SPECIFIED in Table 1 (SEE D3.2 in Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
Measure the thickness of any part that can be reached by the Angle of a 20mm diameter ball in the basic measurement plane on the main surface using the appropriate method given in Appendix B. The minimum thickness of the coating shall meet the requirements specified in Table 1. In the case that the main surface area of the workpiece is equal to or greater than 100mm2, the minimum thickness in the table shall be regarded as the local thickness minimum. In the case that the main surface area of the workpiece is less than 100mm2, the minimum thickness in the table should be regarded as the minimum average thickness.
For printed circuit boards with plated through-holes, the minimum coating thickness requirement applies not only to any position on the main surface that can be reached by a 20mm diameter ball Angle, but also to the surface inside the through-holes (see B0.2.6 in Appendix B).
The thickness requirements for hot melt coatings apply only to coatings in the pre-hot melt state (see D3.2,D4 and Appendix B in Appendix D).
When the thickness measurement is in dispute, the arbitration method specified in B0.2 of Appendix B shall be adopted.
10.3 Ingredients
This standard is based on coatings with tin content in the range of 50% la 70%(raportul de masă).
The nominal tin content should be indicated in the grading number and the composition tolerance should also be indicated in the information provided to the plating party (Vezi nota).
The ANALYTICAL METHOD for TIN – lead coatings is given in Appendix A(STANDARD appendix) and should be used in case of dispute.
Notă: Appendix D gives guidelines for the application of other constituent alloys.
10.4 Bond strength
If the Demander prescribes a test for bonding strength, the test shall be carried out by one of the methods described in Appendix c(STANDARD Appendix) without any indication of detachment of the coating from the substrate.
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
10.5 Porosity
If the Buyer specifies porosity measurement, the coating with a minimum thickness of 10µm or more shall be subjected to one of the following tests, with the number of test cycles to be agreed upon by the supplier and the demand:
A) The iron matrix was tested according to GB/T10125;
b) Non-iron matrix was tested according to GB/T9789.
In both cases, there should be no evidence of substrate corrosion when the test coating is viewed with a 3X magnification (see D1 in Appendix D).
10.6 Welding Performance (see D2 in Appendix D)
10.6.1 General Materials and Parts
If the Demander specifies welding performance testing, the welding performance testing shall be carried out with inactive flux according to Method 1 of Ta test in GB/T2423.28-1982.
If there is a requirement for accelerated aging prior to the test, the aging procedure shall be specified by the purchaser.
ISO 7587-1986 Tablou de acoperire metalic _ Galvanizare din aliaj de aluminiu
10.6.2 Printed circuit board
If the Demander specifies welding performance testing, the printed circuit board coatings conforming to this standard shall be tested for welding performance according to the Tc test in GB/T2423.28-1982.
If there is a requirement for accelerated aging prior to the test, the aging procedure shall be specified by the purchaser.
