ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
úvod
ISO (Mezinárodní organizace pro normalizaci) je globální federací národních normalizačních orgánů (členy ISO). Vývoj mezinárodních norem se obvykle provádí prostřednictvím technických komisí ISO. Each member group interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on the Committee. Mezinárodní organizace, governments and non-governmental organizations in contact with ISO are also involved in this work. ISO úzce spolupracuje s Mezinárodní elektrotechnickou komisí (IEC) ve všech záležitostech elektrické normalizace.
Část 1 Směrnice ISO/IEC popisuje postupy použité pro vývoj tohoto dokumentu a pro další údržbu. Zejména, pozornost by měla být věnována různým schvalovacím kritériím požadovaným pro různé typy dokumentů ISO. Tento dokument byl vypracován v souladu s redakčními pravidly části směrnice ISO/IEC 2 (viz iso.org/directives).
Upozorňujeme, že některé prvky tohoto dokumentu mohou být předmětem patentových práv. ISO nenese odpovědnost za identifikaci některého nebo všech takových patentů. Details of any patent rights identified during the development of the document will be found in the introduction and/or list of ISO Patent declarations received (viz iso.org/patents).
Any trade names used in this document are provided as information for the convenience of the user and do not constitute an endorsement.
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
Voluntary interpretation, related standards and conformity assessment related ISO specific terminology and express the meaning of and the ISO in the technical barriers to trade (TBT) dodržovat principy světové obchodní organizace (WTO) information, please see the iso.org/iso/foreword.html.
This document was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 35, Barvy a laky, Podvýbor SC 9, Common Test Methods for paints and varnishes.
A list of all the parts in the ISO 22553 sérii lze nalézt na webových stránkách ISO.
Any feedback or questions on this document should be referred to the user’s national standards body. A complete list of these institutions can be found at iso.org/members.html.
představit
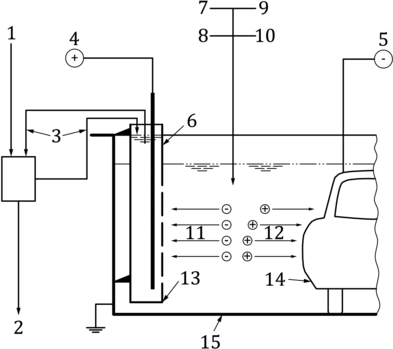
In the electrodeposition coating process, the non-volatile substances in the water-dilutive electrodeposition coating are deposited on the workpiece by the electrophoretic process. During this process, the internal and external areas of the workpiece, including all cavities, are touched. Cathode deposition or anode deposition is distinguished according to whether the workpiece is used as cathode or anode. The cathodic electrodeposition coating process is commonly used (viz obrázek 1).
Postava 1 – Example of the deposition process during cathodic electrodeposition coating
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
Key
| 1个 | Softening water | 9 | solvent |
| 2个 | Wastewater treatment | 10 | Softened water |
| 3个 | Anodic fluid cycle | 11 | acid |
| 4个 | Anode | 12 | Electrodeposition coating |
| 5个 | Cathode | 13 | Ion selective membrane |
| 6个 | Anode box | 14 | tělo |
| 7 | Binder | 15 | Cathodic electrophoresis cell |
| 8个 | pigment |
Through the combination of adhesives, pigments and deposition processes, hardening creates a very corrosion-resistant coating on the workpiece, which contributes significantly to corrosion protection in both internal and external areas.
The electrical properties of the material are also important for the electrical energy consumption (bulk charge density) of the process.
Since the electrophoretic paint is jointly responsible for the overall appearance of the coating system, it is often emphasized that the coating works well and has no visible defects.
Proto, for extensive corrosion protection and sealing of the workpiece, additional joint sealing materials, adhesives or foams are recommended.
Inside the electrophoresis tank, bacterial contamination may be present due to the material being dragged in and the physical conditions (heat, water-based media, carbon sources, atd.).
This document specifies the terms and definitions of electrodeposited coatings. The subsequent part of the ISO 22553 series specifies methods of characterization and testing of electrodeposited coatings. An overview of the test methods is given in Annex A.
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
1 Rozsah aplikace
This document defines the terms for electrodeposited coatings.
It is suitable for electrodeposition coatings in the automotive industry and other general industrial applications, such as chiller, consumer goods, radiators, kosmonautika, zemědělství.
2 Normativní referenční dokumenty
There are no normative references in this document.
3 termíny a definice
3.1 Volume charge density ρ
Quotient of charge Q and volume V, as shown in the formula:
Barvy a laky – electrodeposited coatings – Část 1: Glossary Diagram 2
Poznámka 1: The volume charge density is expressed in coulombs per cubic meter (C/m 3).
Article Note 2:1 C/m 3 = 1 A⋅s/m 3.
3.2 Deposition voltage u
The voltage is adjusted on the corresponding device to deposit an electrodeposited coating material (3.9) by an anode or cathode method, having a film thickness specified for the coating material
Poznámka 1: The deposition voltage is measured in volts (PROTI).
3.3 Deposition time
The time required to obtain the desired film thickness
3.4 Anode electrodeposition coating process
Anodic electrophoresis process
A variant of an electrodeposited coating in which the coated components are connected as an anode and the reverse electrode is connected as a cathode
3.5 Pigment content, determined by ashing
Mass fraction of residue after ashing of the product under specified conditions
Poznámka 1: It includes inorganic pigments, plniva, and other solid components of the product that do not evaporate under test conditions, but their state may change.
3.6 Baking Process
The final drying and chemical crosslinking process of the applied paint film is initiated by heating
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
3.7 Baking loss
Volatiles released under standard baking conditions
Poznámka 1: Baking loss includes reaction loss.
3.8 Entry Tags
Visible defects that occur during the immersion of the panel under voltage, usually in the form of streaks parallel to the bath surface on the object to be painted
Example:
Hash marks (viz obrázek 5), dírky (viz obrázek 4), mappings (viz obrázek 3).
3.9 Elektrolyticky nanesené povlaky
Electronic coating
Waterborne coatings for electrophoretic coating
3.10 Deposition time
The time that voltage is applied between anode and cathode during the coating process
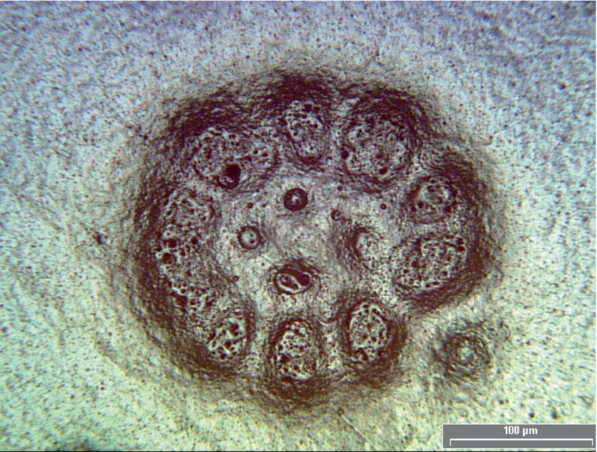
3.11 Flores
Flower-shaped craters, formed by a combination of single craters
Poznámka ke vstupu 1: See Figure 2 for an example.
Postava 2 – Flores’ example
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
3.12 Ochrana hran
The ability to protect edges from corrosion
Article Note 1: Edges may be produced by drilling, děrování, and cutting.
3.13 Edge corrosion
Corrosion due to inadequate edge protection (3.12)
Article Note 1: Edges may be produced by drilling, děrování, and cutting.
3.14 Cathode electrodeposition coating process
Cathodic electrophoresis
A variant of an electrodeposited coating in which the coated parts are connected as a cathode and the reverse electrode is connected as an anode
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
3.15 Bacteria count
Colony count
The number of colony forming units (CFU) to form a macroscopically countable colony
3.16 Mapping
Local differences in film thickness in electrodeposited films
Poznámka ke vstupu 1: See Figure 3 for an example.
Postava 3 – Mapping example

ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
3.17 Pinholes
The holes in the coating extend all the way to the substrate
Article Note 1: Pinholes are often mixed with craters.
Poznámka ke vstupu 2: See Figure 4 for an example.
Postava 4 – pinhole example

3.18 Hash tag
Hydrogen attached during the process causes characteristic depressions in the electrodeposited coating
Item Note 1: One characteristic of the pound sign is the direction of the horizontal line. Zejména, hash marks appear when the specimen is heavily impregnated.
Poznámka ke vstupu 2: See Figure 5 for an example. A distinct hash mark can be detected on the right side that has been moistened with softening water. On the left side of the department, there are significantly fewer hash marks.
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba

3.19 Stability
Electrodeposited coatings are often exposed to the aging process, especially during extended downtime (holidays, downtime, atd.), jako:
– evaporation of water, solvents and neutralizers;
– Chemical changes in adhesives caused by air;
— bring in bacteria;
– Other reactions of the adhesive
3.20 Effort
The ability of the electrodeposited coating to penetrate the box section
3.21 Workpieces
Objects coated with material
ISO 22553-1- Barvy a laky elektrolyticky vylučované povlaky – Část 1: Slovní zásoba
Example:
Trubky, radiators, vehicles, steel test plates, magnesium and aluminum alloys, pre-treated plastics.
3.22 Rupture voltage
Electrodeposition coatings deposit a potential that is no longer controllable, například, a significant change in film thickness, gas formation, or heat generation
Poznámka 1: The rupture voltage can only be determined experimentally by the voltage series.
Veřejná je pouze standardní informační sekce. Chcete-li zobrazit celý obsah, musíte si standard zakoupit prostřednictvím oficiálních kanálů.
