ISO 22553-7-2020, Farben und Lacke – Elektrotauchlacke – Teil 7: Nassfilmbeständigkeit
Vorwort
ISO (Internationale Standardisierungsorganisation) ist der globale Verband nationaler Normungsgremien (ISO-Mitgliedsorganisationen). Die Entwicklung internationaler Standards erfolgt in der Regel durch technische Komitees der ISO. Jede Mitgliedsgruppe, die sich für ein Thema interessiert, zu dem ein Fachausschuss eingerichtet wurde, hat das Recht, im Ausschuss vertreten zu sein. International, An dieser Arbeit sind auch staatliche und nichtstaatliche Organisationen in Zusammenarbeit mit der ISO beteiligt. ISO arbeitet eng mit der International Electrotechnical Commission zusammen (IEC) in allen Fragen der elektrischen Normung.
Teil 1 of the ISO/IEC Directive describes the procedures used to develop this document and for further maintenance. Insbesondere, Beachten Sie die unterschiedlichen Genehmigungsstandards, die für verschiedene Arten von ISO-Dokumenten erforderlich sind. This document has been drafted in accordance with the editorial rules in Part 2 der ISO/IEC-Richtlinie (siehe iso.org/directives).
Please note that some elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. ISO ist nicht dafür verantwortlich, einige oder alle dieser Patente zu identifizieren. Details of any patent rights identified during the documentation development process will be included in the introduction and/or list of ISO patent claims received (siehe iso.org/patents).
Any trade names used in this document are information provided for the convenience of the user and do not constitute an endorsement.
Explanations of the relevant standards of voluntary, ISO specific terms related to conformity assessment and the expression of meaning, and the ISO in the technical barriers to trade (TBT) adhere to the principle of the world trade organization (WTO) Information, please refer to the iso.org/iso/foreword.html.
This document has been prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 35, Farben und Lacke, Unterausschuss SC 9, Common Test Methods for Paints and varnishes.
Eine Liste aller Teile in der ISO 22553 Serien finden Sie auf der ISO-Website.
Any feedback or questions on this document should be referred to the user’s national standards body. A complete list of these institutions can be found at iso.org/members.html.
ISO 22553-7-2020, Farben und Lacke – Elektrotauchlacke – Teil 7: Nassfilmbeständigkeit
einführen
Wet film resistivity provides information about the deposition behavior of electrodeposited coatings, das ist, information about film thickness and film thickness variation, homogeneous plating capacity, and possibly deposition properties under specific conditions.
1 Geltungsbereich
This document specifies a method for determining the resistivity of wet films of electrodeposited coatings (e-coat) for the automotive industry and other general industrial applications (z.B. cooling units, consumer products, radiators, Luft- und Raumfahrt, Landwirtschaft).
2 Normative Referenzdateien
When the following documents are referenced in the context, part or all of them constitute the requirements of this document. Für datierte Referenzen, Es gelten Nur-Zitat-Versionen. Für undatierte Zitate, the most recent version of the referenced document (including any amendments) gilt.
ISO 1514, Farben und Lacke — Standard plates for testing
ISO 4618, Farben und Lacke – Begriffe und Definitionen
ISO 22553-1, Farben und Lacke – electrodeposited coatings – Teil 1: Wortschatz
ISO 23321, Paints and varnishes solvents – softening water for industrial applications – Spezifikation und Testmethoden
3 Begriffe und Definitionen
Für die Zwecke dieses Dokuments, die in der ISO angegebenen Begriffe und Definitionen 4618, ISO 22553-1 und unten gelten.
3.1 Resistance R
The ratio of the potential difference along a conductor to the current through it
Eintragshinweis 1: Resistance is given by Ohm’s law as shown in formula (1) :
![]()
u is the potential difference;
I is current.
The unit of resistance is ohm (Oh), given by the following formula:
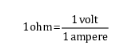
Resistance depends on the material, Größe (length and cross section) and temperature of the conductor.
[Quelle: ISO 15091:2019, 3.1]
3.2 Resistivity ρ
Cross-sectional area The resistance per unit length of a material
Artikelhinweis 1: Resistivity is given by formula (2) :
![]()
A is the cross-sectional area of the conductor;
I is the length of the conductor.
Resistivity is measured in ohms · meters (Ω·m).
[Quelle: ISO 15091:2019, 3.2]
3.3 Wet film resistance Rw
Measure the total resistance (3.1) of electrodeposited coatings, including substrates, pretreatments, and other coatings
Notiz 1: When measuring resistance, technical measurement conditions also have an effect, z.B. membrane, measuring electrode.
Notiz 2 The unit of wet film resistance is ohm (Oh).
3.4 Dynamic wet film resistance
![]()
The measured total resistance (3.1) of the electrodeposited coatings (including substrates, pretreatments, and other coatings) is a function of deposition time
Notiz 1 The unit of wet film resistance (3.3) is ohm (Oh).
3.5 Electrostatic wet film resistance
![]()
Measure the total resistance (3.1) of the electrodeposited coatings, including substrates, pretreatments and other coatings read out at the end of deposition time
Notiz 1 The unit of wet film resistance (3.3) is ohm (Oh).
3.6 Wet film resistivity ρw
The wet film resistance (3.3) is multiplied by the electrode area relative to the distance between the electrodes
Notiz 1: Wet film resistivity is given by formula (3) :
![]()
Rw is wet film resistance;
A is the area of the electrode;
l is the length of the conductor.
The unit of wet film resistivity is ohm ·m (Ω·m).
3.7 Electrical conductivity γ
Reciprocal of resistivity (3.2)
Notiz 1: The conductivity is given by formula (4) :
![]()
The unit of conductivity is Siemens · m-1 (S · m-1).
[Quelle: ISO 15091:2019, 3.4]
Nur der Standardinformationsbereich ist öffentlich. Um den vollständigen Inhalt zu sehen, Sie müssen den Standard über die offiziellen Kanäle erwerben.
