ISO 6603-2-2000 “Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di materie plastiche plastiche dure – Parte 2: Prova di impatto dello strumento”
prefazione
ISO (Organizzazione internazionale per la standardizzazione) è un'alleanza globale di organismi di normalizzazione nazionali (Organismi membri dell'ISO). Lo sviluppo di standard internazionali viene solitamente effettuato attraverso i comitati tecnici ISO. Ciascuna istituzione associata interessata ad una materia sulla quale è stato costituito un comitato tecnico ha il diritto di essere rappresentata in tale comitato. In questo lavoro sono coinvolte anche organizzazioni internazionali governative e non governative che collaborano con l'ISO. L'ISO lavora a stretto contatto con la Commissione Elettrotecnica Internazionale (CEI) su tutte le questioni di standardizzazione elettrotecnica.
Le norme internazionali sono redatte in conformità alle regole riportate nella Part 3 della Direttiva ISO/IEC.
I progetti di standard internazionali adottati dal Comitato Tecnico saranno distribuiti agli organi membri per la votazione. La pubblicazione come standard internazionale richiede l'approvazione di almeno 75% degli organi membri.
Please note that some elements of this section of ISO 6603 Può essere oggetto di diritti di brevetto. L'ISO non è responsabile dell'identificazione di alcuni o tutti questi brevetti.
Norma internazionale ISO 6603-2 è stato sviluppato dal Comitato Tecnico ISO/TC 61, Plastica, Sottocommissione SC 2, Proprietà meccaniche.
The second edition cancelled and replaced the first edition (ISO 6603-2:1989), which had been technically revised.
ISO 6603 consists of the following parts under the general heading Plastics – Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di plastiche rigide:
— Parte 1: Prove di impatto non strumentale
— Parte 2: Instrumental impact testing
The appendices A to E of this part of ISO 6603 are for reference only.
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di materie plastiche plastiche dure – Parte 2: Prova di impatto dello strumento”
1 allineare
Questa parte dell'ISO 6603 specifies a test method for determining puncture impact properties of rigid plastics in the form of flat specimens using instruments that measure force and deflection. Applies if a force-deflection or force-time plot recorded at a nominal constant firing pin speed is necessary to characterize impact behavior in detail.
If ISO 6603-1 is sufficient to characterize the impact behavior of plastics by impact failure energy thresholds based on many samples, ISO 6603-1 May be used.
Questa parte dell'ISO 6603 is not intended to explain the mechanisms that occur at each particular point in the force-deflection diagram. These explanations are the task of scientific research.
Note also article 1 dell'ISO 6603-1:2000.
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di materie plastiche plastiche dure – Parte 2: Prova di impatto dello strumento”
2 referenze normative
The following normative documents contain provisions which, per riferimento qui, costituiscono le disposizioni di questa parte della ISO 6603. Per riferimenti datati, non verranno applicate revisioni o modifiche successive a queste pubblicazioni. Tuttavia, Parti di un accordo basato su questa parte dell'ISO 6603 are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the latest version of the following normative documents. Per riferimenti non datati, the latest version of the normative document referred to applies. I membri di ISO e IEC mantengono un registro degli standard internazionali attualmente in vigore.
ISO 2602:1980, Statistical interpretation of test results – mean Estimators – confidence intervals.
ISO 6603-1:2000, Plastica. Determination of puncture impact behavior of rigid plastics. Parte 1: Non-instrumental impact tests.
3 Termini e definizioni
Ai fini di questa parte dell'ISO 6603, si applicano i seguenti termini e definizioni.
3.1 Velocità d'impatto
The speed of the firing pin relative to the support at impact
Nota 1: The impact velocity is expressed in meters per second (SM).
3.2 Force F
The force exerted by the firing pin on the specimen in the direction of impact
Nota 1: Force is expressed in Newtons (N).
3.3 Deflection l
The relative displacement between the firing pin and the specimen support starts from the first contact between the firing pin and the specimen
Nota 1: Deflection is expressed in millimeters (mm).
3.4 Energy
Energy used to deform and penetrate the specimen up to the deflection L
Nota 1: Energy is expressed in joules (J).
Nota 2 The energy is measured as the integral of the force-deflection curve from the point of impact to the deflection l.
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di materie plastiche plastiche dure – Parte 2: Prova di impatto dello strumento”
3.5 Maximum power FM
The most power that occurs during the test
Nota 1: The maximum force is expressed in Newtons (N).
3.6 Deflection lm at maximum force
Deflection at maximum force FM
Nota 1 Deflection at maximum force is expressed in millimeters (mm).
3.7 Energy to maximum strength
The energy expended at maximum force reaches deflection lM
Nota 1: The most powerful energy is expressed in joules (J).
3.8 Puncture deflection lP
The force is reduced to half the deflection of the maximum force F M
See Figures 1-4 E 3.9 notes.
Nota 1 Puncture deflection is expressed in millimeters (mm).
3.9 Puncture energy
Energy expended until the puncture deflects lP
See Figures 1 through 4 and note 2.
Nota 1: Puncture energy is expressed in joules (J).
Nota 2 A probe mounted at a distance from the impact tip records the friction force acting between the cylindrical part of the firing pin and the piercing material when testing hard materials. The corresponding friction energy should not be included in the piercing energy, so the piercing energy is limited to that deflection, where the force drops to half of the maximum force FM.
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di materie plastiche plastiche dure – Parte 2: Prova di impatto dello strumento”
3.10 Impact Failure
Mechanical properties of the material to be measured, which may be of one of the following types (see note) :
UN) YD yIELDING (zero slope at maximum power), then DEEP yielding
B) YS yIELDING (Zero slope at maximum power) Poi (at least partially) cracked the S bench
C) yIELDING of Yu (zero slope at maximum power) Then u unstable cracking
D) no yielding for new features
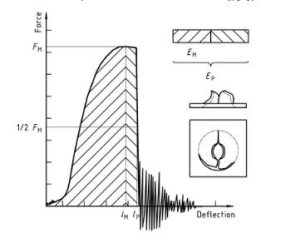
Nota 1: A comparison of Figures 2 E 3 shows that puncture deflections l, P and puncture energy EP are the same for failure types YS and YU. As shown in Figure 4, in the case of failure type YU, the deflection and energy values are the same at maximum and puncture. For complex behaviour, vedere l'allegato A.
Figura 1 — An example of a force-deflection diagram of the typical appearance of a specimen after deep drawing and testing (using lubrication) through yield (zero slope at maximum force)
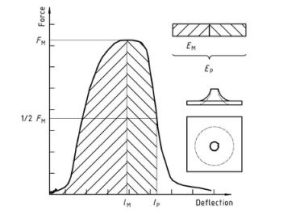
Plastica – Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di plastiche rigide – Parte 2: Instrument impact test Diagram 1
Figura 2 — Example force-deflection plot of failure by yield (zero slope at maximum force), followed by steady crack growth, and typical appearance of the specimen after testing (using lubrication)
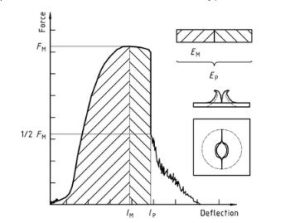
Plastica – Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di plastiche rigide – Parte 2: Instrument impact test diagram 2
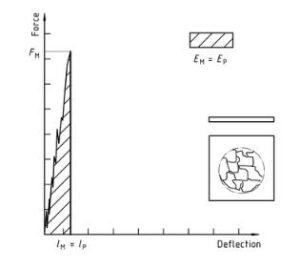
Figura 3 — Examples of force-deflection plots through yield (zero slope at maximum force) and typical appearance (lubrication) failure of a tested specimen
Plastica – Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di plastiche rigide – Parte 2: Instrument impact test diagram 3
Note that the natural vibration of the force detector can be seen after the unstable cracking (firing pin and weighing sensor).
Figura 4 — An example force-deflection diagram of an unyielding failure followed by unstable crack growth and a typical appearance of the specimen after testing (using lubrication)
Plastica – Determinazione del comportamento all'impatto con foratura di plastiche rigide – Parte 2: Instrument impact test diagram 4
Solo la sezione informativa standard è pubblica. Per vedere il contenuto completo, è necessario acquistare lo standard attraverso i canali ufficiali.
