ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
導入
ISO (国際標準化機構) 国家標準化団体の世界的な同盟です (ISO会員団体). 国際規格の開発は通常、ISO 技術委員会を通じて行われます。. 技術委員会が設立された主題に関心を持つ各加盟機関は、その委員会に代表される権利を有する。. ISO と連携する国際政府および非政府組織もこの作業に関与しています。. ISO は国際電気標準会議と緊密に連携しています。 (IEC) 電気の標準化に関するあらゆる問題について.
国際規格は、第 1 部に記載されている規則に従って草案されます。 3 ISO/IEC 指令の.
技術委員会によって採択された国際規格草案は、投票のために加盟団体に配布されます。. 国際標準として発行するには、少なくとも承認が必要です 75% 加盟機関の.
ISO のこの部分のいくつかの要素に注意してください。 6603 特許権の対象となる可能性がある. ISO は、そのような特許の一部またはすべてを特定する責任を負いません。.
国際規格ISO 6603-1 was developed by the Technical Committee ISO/TC61, プラスチック, 分科会SC 2, Mechanical Properties.
ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
第 2 版は、技術的に改訂された第 1 版をキャンセルし、置き換えます。 (ISO 6603-1:1985).
ISO 6603 以下の部分で構成されています, under the general heading Plastics – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定:
– 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験
– 一部 2: Instrumented impact testing
ISO のこの部分の付録 A 6603 is for information purposes only.
1 範囲
This standard specifies a method for determining, under specified conditions, the puncture impact properties of rigid plastics in the form of flat specimens, such as disks or squares. The sample can be molded directly, cut from the sheet or removed from the finished product. Different types of samples and test conditions are defined.
ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
These drop dart methods are used to study the behavior of plastic films or molds under the impact of a firing pin perpendicular to the specimen plane.
ISO のこの部分 6603 can be used if it is sufficient to characterize the impact behavior of plastics by an impact failure energy threshold based on many samples. If a force-deflection or force-time plot recorded at a nominal constant firing pin speed is necessary to characterize impact behavior in detail, ISO 6603-2 使用されている.
These test methods are suitable for specimens with thicknesses between 1 mmと 4 んん.
Note For thicknesses less than 1 んん, ISO 7765 is recommended. If the equipment is suitable, it is possible to test thicknesses greater than 4 んん, but this test falls outside the scope of ISO 6603-1 およびISO 6603-2.
These methods are suitable for the following types of materials:
Rigid thermoplastic molding and extrusion materials, including filled, unfilled and reinforced compounds and sheets;
– Rigid thermosetting molding and extrusion materials, 充填および補強コンパウンドを含む, sheets and laminates;
ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
Fiber-reinforced thermoset and thermoplastic composites, including unidirectional or non-unidirectional reinforcement materials, such as MATS, woven fabrics, woven roving, cut strands, combined and mixed reinforcement materials, roving, milled fibers and sheets made from pre-impregnated materials (prepregs).
These methods are also applicable to samples molded or machined from finished products, laminates and extruded or cast plates.
The test results are comparable only when the preparation conditions, size and surface of the sample and the test conditions are the same. 特に, the results determined on specimens of different thicknesses cannot be compared with each other (see Appendix E: – ISOへの変換 6603-2). A comprehensive assessment of the impact stress response requires measurement of the impact velocity and temperature of different material variables, such as crystallinity and moisture content.
The impact behavior of the finished product cannot be predicted directly from this test, but samples can be taken from the finished product (see above) for testing by these methods.
Test data developed through these methods should not be used in design calculations. しかし, information on the typical behaviour of the material can be obtained by testing at different temperatures and impact velocities (see Annex D of ISO 6603-2: -), varying thickness (see Annex E of ISO 6603-2: -) and testing samples prepared under different conditions.
ISO のこの部分 6603 describes two statistical test methods:
– 方法A: Staircase Method (Individual) (preferred)
In this method, a uniform energy increment is used during the test. After testing each sample, the energy is reduced or increased by uniform increments, depending on the observations (pass or fail) of the previous test.
ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
– 方法B: Group method (オプション)
In this method, a continuous group of at least ten samples is tested. The impact failure energy is calculated statistically.
2 規範的参照
以下の規範文書には、以下の規定が含まれています。, ここでの参照により, ISO のこの部分の規定を構成します 6603. 日付の付いた参照については, これらの出版物に対するその後の改訂または修正は適用されません。. しかし, ISO のこの部分に基づく協定の当事者 6603 以下の規範文書の新しいバージョンを適用する可能性を調査することが推奨されます。. 日付のない参考文献については, 参照されている標準設定文書の新しいバージョンが適用されます. ISO および IEC メンバーは、現在有効な国際規格の登録簿を維持しています。.
ISO 291:1997, プラスチック. Adjust and test the standard atmosphere.
ISO 293:1986, プラスチック. Compression forming sample of thermoplastic material.
ISO 294-3:1996, プラスチック. 熱可塑性プラスチック材料サンプルの射出成形. 一部 3: Small board.
ISO 295:1991, プラスチック. Compression molding of thermosetting material samples.
ISO 1268:19741), プラスチック – Preparation of glass fiber reinforced, resin bonded, low pressure laminates or panels for test purposes.
ISO 2818:1994, プラスチック. The sample was prepared by machining.
ISO 7765-1:1988, plastic films and sheets. The impact resistance was determined by the free falling dart method. 一部 1: Staircase method.
ISO 7765-2:1994, plastic films and sheets. The impact resistance was determined by the free fall dart method. 一部 2: Instrumental puncture test.
ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
3 用語と定義
For the purposes of this part of ISO 6603, 次の用語と定義が適用されます:
3.1 概要
3.1.1 Failure
Any visible breakage of the specimen surface
3.2 Failure standard terms
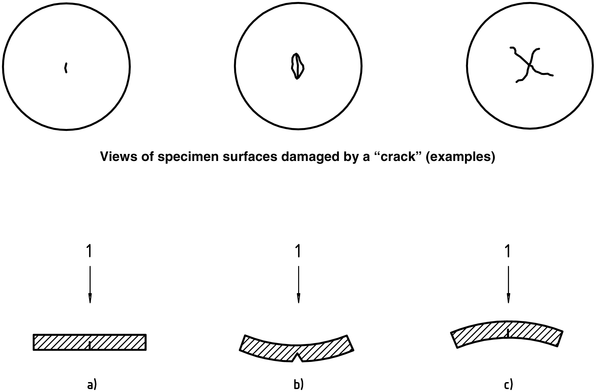
3.2.1 Crack
Any cracks that are visible to the naked eye and cannot penetrate the entire thickness of the material
見る: 形 1
3.2.2 Broken
Any cracks throughout the entire thickness of the material
見る: 形 2
3.2.3 Penetration
Failure of the firing pin to penetrate the entire thickness of the specimen
見る: 形 3 b)
3.2.4 研削
Break the sample into two or more pieces
見る: 形 3 ある)
3.3 Impact failure items
3.3.150 % impact failure energy E50
The energy that causes 50% of the sample to fail, as defined in 3.1.1
3.3.250 % impact failure mass M50
The mass that causes 50% of the sample to fail at a given fall height, as defined in 3.1.1
3.3.350 % impact failure mass H50
50% impact failure height H50 uses the height at which a given falling mass causes 50% sample failure, as defined in 3.1.1
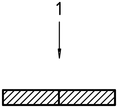
形 1 – Specimen sections damaged by “ひび割れ” [b) and c) after bending by hand
| 1 | Impact direction |
ISO 6603-1-2000 “プラスチック – 硬質プラスチックの穿刺衝撃挙動の測定 – 一部 1: 非器具衝撃試験”
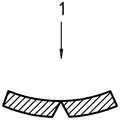
形 2 – Slices passed through the specimen are damaged by “breakage” [b) and c) after bending by hand
| ある)
| b)
| c)
|
| 1 | Impact Direction |
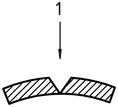
形 3 – Examples of “broken” failures [ある) そして “penetrated” [b)
ある)
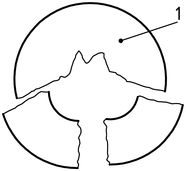
b)
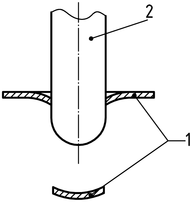
| 1 | 検体 |
| 2 | Darts with hemispherical heads |
標準情報部分のみ公開. 完全なコンテンツを表示するには, 公式チャネルを通じて標準を購入する必要があります.