ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
introducere
ISO (Organizația Internațională pentru Standardizare) este o alianță globală a organismelor naționale de standardizare (organismele membre ISO). Elaborarea standardelor internaționale se realizează de obicei prin intermediul comitetelor tehnice ISO. Fiecare instituție membră interesată de un subiect pe care a fost înființat un comitet tehnic are dreptul de a fi reprezentată în respectivul comitet. Organizațiile internaționale guvernamentale și neguvernamentale care au legătură cu ISO sunt, de asemenea, implicate în această activitate. ISO lucrează îndeaproape cu Comisia Electrotehnică Internațională (IEC) în toate problemele de standardizare electrică.
Standardele internaționale sunt elaborate în conformitate cu regulile prevăzute în partea 3 din Directiva ISO/IEC.
Proiectul standardului internațional adoptat de Comitetul Tehnic va fi transmis organelor membre pentru vot. Publicarea ca standard internațional necesită aprobarea de cel puțin 75% a instituţiilor membre.
Please note that some elements of this part of ISO 6603 Poate face obiectul unui drept de brevet. ISO nu este responsabil pentru identificarea unuia sau a tuturor acestor brevete.
Standardul internațional ISO 6603-2 a fost dezvoltat de Comitetul Tehnic ISO/TC 61, Materiale plastice, Subcomisia SC 2, Mechanical Properties.
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
A doua ediție anulează și înlocuiește prima ediție (ISO 6603-2:1989), care a fost revizuit tehnic.
ISO 6603 constă din următoarele părți, under the general heading Plastics – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide:
– Parte 1: Testare de impact non-instrumentală
– Parte 2: Instrumented impact testing
Appendices A to E of this part of ISO 6603 are for information purposes only.
1 Gamă
Această parte a ISO 6603 specifies a test method for determining the puncture impact properties of rigid plastics in the form of flat specimens using instruments that measure force and deflection. This applies if a force-deflection or force-time plot recorded at a nominal constant firing pin speed is necessary to characterize impact behavior in detail.
ISO 6603-1 can be used if ISO 6603-1 is sufficient to characterize the impact behavior of plastics by an impact failure energy threshold based on many samples.
The purpose of this part of ISO 6603 is not to explain the mechanisms that occur at each particular point on the force-deflection chart. These explanations are the task of scientific research.
Note also Article 1 of ISO 6603-1:2000.
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
2 referințe normative
The following normative documents contain provisions that, by reference herein, constitute the provisions of this part of ISO 6603. Pentru referințe datate, any subsequent revisions or amendments to these publications will not apply. in orice caz, Parties to agreements based on this part of ISO 6603 sunt încurajați să investigheze posibilitatea aplicării unor noi versiuni ale următoarelor documente normative. Pentru referințe nedatate, a new version of the standard-setting document referred to applies. Membrii ISO și IEC țin un registru al standardelor internaționale valabile în prezent.
ISO 2602:1980, Statistical interpretation of test results – mean estimation – confidence intervals.
ISO 6603-1:2000, Materiale plastice. Determination of puncture impact behavior of rigid plastics. Parte 1: Non-instrumental impact tests.
3 Termeni și definiții
For this part of ISO 6603, se aplică următorii termeni și definiții.
3.1 Impact velocity
The speed of the firing pin relative to the support at the time of impact
Notă 1: The impact velocity is expressed in meters per second (Domnișoară).
3.2 Force F
The force exerted by the firing pin on the specimen in the direction of impact
Notă 1: Force is expressed in Newtons (N).
3.3 Deflection l
The relative displacement between the firing pin and the specimen holder begins with the first contact between the firing pin and the specimen
Notă 1: Deflection is expressed in millimeters (mm).
3.4 Energy
The energy expended to deform and penetrate the specimen up to the deflection L
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
Notă 1: Energy is expressed in joules (J).
Notă 2: The energy is measured as the integral of the force-deflection curve from the point of impact to the deflection l.
3.5 Maximum Power FM
The test process occurs with maximum force
Notă 1: Maximum force is expressed in Newtons (N).
3.6 Deflection lm at maximum force
Deflection at maximum power FM
Notă 1: Deflection under maximum force is expressed in millimetres (mm).
3.7 Energy to maximum power
The energy expended at maximum force reaches deflection lM
Notă 1: The most powerful energy is expressed in joules (J).
3.8 Puncture deflection lP
The force is reduced to half the deflection of the maximum force F M
See Figures 1-4 and Note 3.9.
Notă 1: Puncture deflection is expressed in millimeters (mm).
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
3.9 Puncture Energy
The energy consumed until the puncture deflects lP
See Figures 1-4 and note 2.
Notă 1: The puncture energy is expressed in joules (J).
Notă 2: When testing hard materials, a probe mounted at a distance from the impact tip can record the friction force acting between the cylindrical part of the firing needle and the piercing material. The corresponding friction energy should not be included in the piercing energy, so the piercing energy is limited to that deflection, where the force drops to half of the maximum force FM.
3.10 Impact Failure
The mechanical properties of the material to be measured may be of one of the following types (Vezi nota) :
| A) | YD | yIELDING(Zero slope at maximum force), followed by DEEP drawing |
| b) | YS | (Zero slope at maximum force) then (at least partially) the S table cracks |
| c) | yu | yIELDING(Zero slope at maximum force) and then u unstable cracking |
| d) | New function | no yielding |
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
Notă 1: A comparison of Figures 2 și 3 shows that puncture deflection lP and puncture energy EP are the same for failure types YS and YU. As shown in Figure 4, in the case of failure type YU, the deflection and energy have the same values at the maximum and at the puncture. For complex behaviour, see annex A.
Figure 1 – An example of a force-deflection diagram of the typical appearance of a specimen after yielding (zero slope at maximum force) followed by deep drawing and testing (using lubrication)
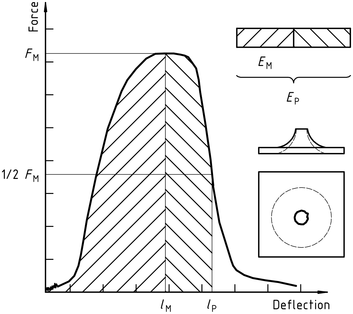
Figure 2 – Example force-deflection diagram of failure by yield (zero slope at maximum force), followed by steady crack growth, and typical appearance of the specimen after testing (using lubrication)
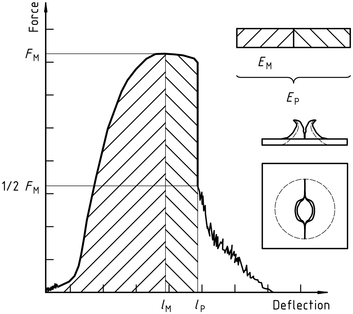
Figure 3 – Example force-deflection diagram of failure through yield (zero slope at maximum force) and the typical appearance (lubrication) of the specimen after testing
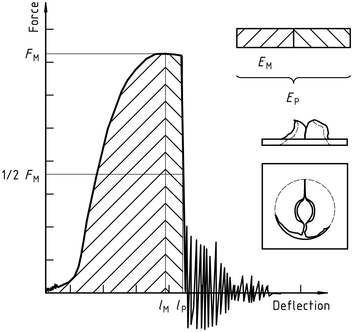
Note the natural vibration of the force detector can be seen after the unstable cracking (firing pin and weighing sensor).
Figure 4 – Example force-deflection diagram of unyielding failure followed by unstable crack propagation and typical appearance of the specimen after testing (using lubrication)
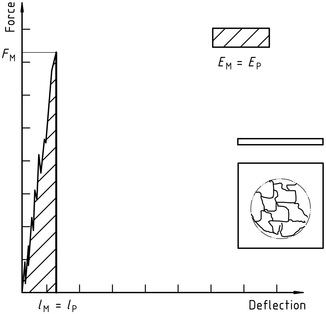
ISO 6603-2-2000 “Materiale plastice – Determinarea comportamentului la impact la perforare a materialelor plastice rigide – Parte 2: Test de impact al instrumentului”
Doar secțiunea de informații standard este publică. Pentru a vedea conținutul complet, trebuie să achiziționați standardul prin canalele oficiale.
