ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
1 ScopeThis STANDARD specifies the technical requirements and test methods for electroplating of Tin-lead alloys with tin content ranging from 50% sa 70%(ratio ng masa) (tingnan sa 10.3).
This STANDARD APPLIES to tin – lead alloy electroplating for preventing corrosion and improving welding performance on electronic and electrical products and other metal products.
This standard is also applicable to tin-lead alloy coatings of other compositions, but it should be noted that the properties of these coatings may differ from those of tin-lead alloy coatings in the above alloy composition range.
The classification method in this standard clearly indicates the category of the base metal and the composition of the coating with a certain tin content range, as well as the provisions of the hot melt layer and bright deposition layer.
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
This standard does not apply to:
a) tin-lead alloy coating on threaded parts;
b) tin-lead alloy coating on bearings;
Tin-lead alloy coating on unworked sheets, strips or wires or on parts formed from them;
d) Tin-lead alloy coating on steel with tensile strength greater than 1000Mpa(or corresponding hardness), as such steel is prone to hydrogen embrittleness after electroplating (tingnan sa 8.2).
2 Mga pamantayan ng sanggunian
The following standards contain provisions which, by reference in this standard, constitute provisions of this Standard. At the time of publication of this standard, all versions shown are valid. All standards are subject to revision and parties using this standard should explore the possibility of using new versions of the following standards.
Basic environmental test procedures for electronic and electrical products Test T: Soldering test method (eqv]EC68-2-20:1979)
Metal coating coating thickness measurement Anode dissolved Coulomb method (idtIs02177:1985)
Test method for adhesion strength of Metal coatings (electrodeposited and chemically deposited) on metal substrates (eqvIS02819:1980)
Light industrial products-test method for thickness of metal coatings and chemically treated coatings — β-ray backscattering method (idtIS03543:1981)
Methods for microscopic measurement of cross-sectional thickness of metal and oxide coatings (eqvIS01463:1982)
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
Sulfur dioxide corrosion test for metals and other non-organic covers under normal condensation conditions (eqvIS06988:1985)
Corrosion test in artificial atmosphere Salt spray test (eqvIS09227:1990)
Methods for chemical analysis of tin-lead solder – Determination of tin content by iodate assay
Definitions and general rules for thickness measurement of metal and other inorganic coatings (eqvIS020 “:1990)
Procedures for Sampling inspection of electrodeposited metal covers and related finishing counts (eqvIs04519:1980)
Metal cover thickness measurement X-ray spectrometry (eqvIS03497:1990)
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
3 Definitions
The following definitions are used in this standard.
3.1 Main surface significantsurface
Some surface on the workpiece that has been or is to be plated, on which the coating is important to the appearance and/or performance of the workpiece and shall meet all the requirements specified in the standard.
3.2 Basic measurement surface refe beginning ncearea
An area of the main surface in which a specified number of single measurements are required.
3.3 Hot melt fl0w-melting
A process USED by molten plating TO improve surface QUALITY to obtain desired properties such as brightness or brazing properties (see D4 in Appendix D(A SUGGESTED APPENDIX)).
Information TO BE PROVIDED BY THE DEMANDER TO THE ELECTROPLATING MANUFACTURER
4.1 Necessary Information
The Demander shall provide the following information to the electroplating manufacturer:
a) This national standard No.
b) properties of the matrix metal (tingnan sa Kabanata 5);
c) Condition number (tingnan sa 7.1) or coating classification number (tingnan sa 7.2) and alloy composition requirements (tingnan sa 10.3); d) Whether the composition of the coating should be tested (tingnan sa 10.3);
d) Specify the main surface of the workpiece to be plated, if marked with drawings or provided with suitably marked samples;
f) Sampling and inspection requirements (tingnan sa Kabanata 6);
g) Unavoidable joint corner traces and other acceptable coating defects on the workpiece (tingnan sa 10.1);
h) the bonding strength test method used (tingnan sa 10.4);
i) Special post-plating treatment (see D3.1 in Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
4.2 Supplementary Information
The Demander may also request the following supplementary information:
a) requirements for heat treatment (tingnan sa Kabanata 8);
b) Porosity test requirements (tingnan sa 10.5);
Brazing test requirements and test methods and conditions of use (tingnan sa 10.6);
d) Special requirements for bottom coatings (tingnan sa Kabanata 9);
) samples indicating the appearance requirements of the coating (see 10.l);
f) special pretreatment requirements;
g) Special packaging requirements for self-plated parts.
Tala: THE Demander shall provide THE contents specified in 4.1 at, if necessary, 4.2. It is not sufficient to provide the number of this Standard without these contents.
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
5 Matrix
This standard does not require the surface state, appearance or surface roughness of the substrate before plating (see D2.1 in Appendix D). But because the substrate surface quality is too poor to make the coating can not meet the appearance and/or performance requirements, can not be considered plating production quality does not meet the requirements.
6 Take samples
When it is necessary to check whether the tIN-lead coating meets the requirements specified in Chapter 10 of this standard, sampling shall be carried out according to the sampling method specified in GB/T12,609, and the acceptance level shall be agreed between the supply and demand parties.
7 Classification
7.1 Use condition number
According to the following conditions of use environment and use condition number to indicate the severity of use conditions:
4 Particularly harsh as used outdoors under harsh corrosive conditions (see D1 in Appendix D);
3 Harsh as typical outdoor temperature conditions;
2 Medium as used for indoor slightly condensation conditions;
Mild AS USED in indoor dry atmosphere conditions, where welding performance is the main requirement. note
1 Tingnan sa 10.2, where guidelines on the relationship between the use of condition numbers and minimum thickness are given.
When THE use condition number or data layer classification number is specified, attention should be paid to the tin _ lead alloy in the ring with abrasives or in some organic volatile vapors
Easily damaged in the environment (see Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
7.2 Coating classification number
The coating grade number is composed of four parts, among which the first two parts shall be separated by a short slash line. Such as fbcd
Saan :a represents the chemical symbol of the matrix metal (or the main component in the alloy matrix);
b represents the chemical symbol of the bottom coating metal (or the main component of the alloy bottom coating), and then the minimum thickness of the bottom coating is represented by a number, in µm, which can be omitted if there is no bottom coating (see 4.2d));
One represents the composition of the coating, the method is the chemical symbol sn and then represents the mass percentage of tin in the coating, and then a short horizontal line and chemical symbol pb, and then the minimum thickness of tin _ lead coating, unit µm;
d 1 represents the finishing state of the coating surface, symbol m is no light coating,b is bright coating,f is hot melt coating.
Halimbawa na lang :Fe/Ni5Sn60-Pb10f the classification number indicates that the base metal is iron and steel, the bottom coating is nickel coating at least 5µm thick, the nominal tin content of tin _ lead coating is 60%(ratio ng masa), at least 10µm thick, and has been hot melt treated.
Heat TREATMENT OF steel
8.1 Stress relief before plating
The deep cold deformation work hardened steel parts should be heat-treated at 190~220℃ for 1h before electroplating. To relieve stress.
After carburizing, flame quenching or high frequency induction quenching and subsequent grinding of some steel, with the above conditions will damage its performance, can be replaced by a lower temperature to eliminate stress, such as 130~150℃, the treatment time is not less than 5h.
8.2 Elimination of hydrogen embritculation after plating
Because the diffusion of hydrogen through the tin-lead coating is very slow, and the coating will melt at the temperature required by the hydrogen removal treatment, the heat treatment to eliminate hydrogen embrittlement is not announced after electroplating.
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
Requirements for the bottom coating
For any of the following reasons, it is necessary to electroplate the bottom coating for some matrix materials:
a) Prevention of diffusion (see D2.2 and D2.3 in Appendix D);
b) Maintain welding performance (see D2.2, D2.3 and D2.4 in Appendix D);
c) Guarantee bond strength (see D2.4 and D2.5 in Appendix D);
d) Improve and f erodibility.
When choosing the bottom coating or the bottom coating system, it should be noted that it should not bring bad performance, such as hydrogen embrittance of the base material or the plated parts, and the use of high stress nickel should be avoided.
If the substrate material is a zinc-containing copper alloy and weldability is required, in addition to the specified tin-lead alloy coating thickness (tingnan sa 10.2), a nickel or copper substrate of a minimum local thickness of 2.5µm is required to maintain good appearance and bond strength (see D2.3 in Appendix D).
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
If a bottom coating is specified, its performance (see Appendix D) and minimum local thickness (tingnan sa 10.2) shall be specified by the Demander.
The thickness of a single or multiple substrate coating shall be measured using the appropriate method specified in Appendix B(Appendix to the standard).
10 Requirements for coating
10.1 Appearance
During visual inspection, there should be no visible defects on the main surface of the plated parts, such as foaming, pinholes, roughness, cracks or local no coating, and there should be no stains or discoloration.
The Demander shall specify acceptable and unavoidable parts of joint corners and allowable defects on non-primary surfaces.
After electroplating, the surface of the workpiece should be clean, no damage, uniform, no nodules, and there should be no non-hole wet zone at the melting place. The reticulate pattern that may appear on the surface cannot be regarded as unqualified.
If necessary, samples indicating the appearance requirements of the coating shall be provided or approved by the demander.
10.2 Ang kapal
The TIN-LEAD COATINGS ARE CLASSIFIED BY THICKNESS AND THE MINIMUM thickness value FOR EACH CONDITION NUMBER (SEE 7.1) IS SPECIFIED in Table 1 (SEE D3.2 in Appendix D).
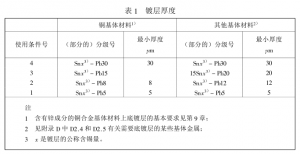
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
Measure the thickness of any part that can be reached by the Angle of a 20mm diameter ball in the basic measurement plane on the main surface using the appropriate method given in Appendix B. The minimum thickness of the coating shall meet the requirements specified in Table 1. In the case that the main surface area of the workpiece is equal to or greater than 100mm2, the minimum thickness in the table shall be regarded as the local thickness minimum. In the case that the main surface area of the workpiece is less than 100mm2, the minimum thickness in the table should be regarded as the minimum average thickness.
For printed circuit boards with plated through-holes, the minimum coating thickness requirement applies not only to any position on the main surface that can be reached by a 20mm diameter ball Angle, but also to the surface inside the through-holes (see B0.2.6 in Appendix B).
The thickness requirements for hot melt coatings apply only to coatings in the pre-hot melt state (see D3.2,D4 and Appendix B in Appendix D).
When the thickness measurement is in dispute, the arbitration method specified in B0.2 of Appendix B shall be adopted.
10.3 Ingredients
This standard is based on coatings with tin content in the range of 50% sa 70%(ratio ng masa).
The nominal tin content should be indicated in the grading number and the composition tolerance should also be indicated in the information provided to the plating party (tingnan sa tala).
The ANALYTICAL METHOD for TIN – lead coatings is given in Appendix A(STANDARD appendix) and should be used in case of dispute.
Tala: Appendix D gives guidelines for the application of other constituent alloys.
10.4 Bond strength
If the Demander prescribes a test for bonding strength, the test shall be carried out by one of the methods described in Appendix c(STANDARD Appendix) without any indication of detachment of the coating from the substrate.
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
10.5 Porosity
If the Buyer specifies porosity measurement, the coating with a minimum thickness of 10µm or more shall be subjected to one of the following tests, with the number of test cycles to be agreed upon by the supplier and the demand:
a) The iron matrix was tested according to GB/T10125;
b) Non-iron matrix was tested according to GB/T9789.
In both cases, there should be no evidence of substrate corrosion when the test coating is viewed with a 3X magnification (see D1 in Appendix D).
10.6 Welding Performance (see D2 in Appendix D)
10.6.1 General Materials and Parts
If the Demander specifies welding performance testing, the welding performance testing shall be carried out with inactive flux according to Method 1 of Ta test in GB/T2423.28-1982.
If there is a requirement for accelerated aging prior to the test, the aging procedure shall be specified by the purchaser.
ISO 7587-1986 Metal cover tin _ Aluminum Alloy electroplating
10.6.2 Printed circuit board
If the Demander specifies welding performance testing, the printed circuit board coatings conforming to this standard shall be tested for welding performance according to the Tc test in GB/T2423.28-1982.
If there is a requirement for accelerated aging prior to the test, the aging procedure shall be specified by the purchaser.
