ISO 22553-7-2020, Paints and varnishes – electrodeposition coatings – Part 7: Wet film resistance
preface
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is the global federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The development of international standards is usually carried out through ISO technical committees. Each member group interested in a subject on which a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on the Committee. International, governmental and non-governmental organizations in liaison with ISO are also involved in this work. ISO works closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrical standardization.
Part 1 of the ISO/IEC Directive describes the procedures used to develop this document and for further maintenance. In particular, note the different approval standards required for different types of ISO documents. This document has been drafted in accordance with the editorial rules in Part 2 of the ISO/IEC Directive (see iso.org/directives).
Please note that some elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. ISO is not responsible for identifying any or all such patents. Details of any patent rights identified during the documentation development process will be included in the introduction and/or list of ISO patent claims received (see iso.org/patents).
Any trade names used in this document are information provided for the convenience of the user and do not constitute an endorsement.
Explanations of the relevant standards of voluntary, ISO specific terms related to conformity assessment and the expression of meaning, and the ISO in the technical barriers to trade (TBT) adhere to the principle of the world trade organization (WTO) information, please refer to the iso.org/iso/foreword.html.
This document has been prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 35, Paints and Varnishes, Subcommittee SC 9, Common Test Methods for Paints and varnishes.
A list of all the parts in the ISO 22553 series can be found on the ISO website.
Any feedback or questions on this document should be referred to the user’s national standards body. A complete list of these institutions can be found at iso.org/members.html.
ISO 22553-7-2020, Paints and varnishes – electrodeposition coatings – Part 7: Wet film resistance
introduce
Wet film resistivity provides information about the deposition behavior of electrodeposited coatings, that is, information about film thickness and film thickness variation, homogeneous plating capacity, and possibly deposition properties under specific conditions.
1 Scope of application
This document specifies a method for determining the resistivity of wet films of electrodeposited coatings (e-coat) for the automotive industry and other general industrial applications (e.g. cooling units, consumer products, radiators, aerospace, agriculture).
2 Normative reference files
When the following documents are referenced in the context, part or all of them constitute the requirements of this document. For dated references, citation-only versions apply. For undated citations, the most recent version of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 1514, Paints and varnishes — Standard plates for testing
ISO 4618, Paints and varnishes – Terms and definitions
ISO 22553-1, Paints and varnishes – electrodeposited coatings – Part 1: Vocabulary
ISO 23321, Paints and varnishes solvents – softening water for industrial applications – Specification and test methods
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO 4618, ISO 22553-1 and below apply.
3.1 Resistance R
The ratio of the potential difference along a conductor to the current through it
Entry Note 1: Resistance is given by Ohm’s law as shown in formula (1) :
![]()
u is the potential difference;
I is current.
The unit of resistance is ohm (Ω), given by the following formula:
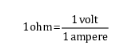
Resistance depends on the material, size (length and cross section) and temperature of the conductor.
[Source: ISO 15091:2019, 3.1]
3.2 Resistivity ρ
Cross-sectional area The resistance per unit length of a material
Item Note 1: Resistivity is given by formula (2) :
![]()
A is the cross-sectional area of the conductor;
I is the length of the conductor.
Resistivity is measured in ohms · meters (Ω·m).
[Source: ISO 15091:2019, 3.2]
3.3 Wet film resistance Rw
Measure the total resistance (3.1) of electrodeposited coatings, including substrates, pretreatments, and other coatings
Note 1: When measuring resistance, technical measurement conditions also have an effect, e.g. membrane, measuring electrode.
Note 2 The unit of wet film resistance is ohm (Ω).
3.4 Dynamic wet film resistance
![]()
The measured total resistance (3.1) of the electrodeposited coatings (including substrates, pretreatments, and other coatings) is a function of deposition time
Note 1 The unit of wet film resistance (3.3) is ohm (Ω).
3.5 Electrostatic wet film resistance
![]()
Measure the total resistance (3.1) of the electrodeposited coatings, including substrates, pretreatments and other coatings read out at the end of deposition time
Note 1 The unit of wet film resistance (3.3) is ohm (Ω).
3.6 Wet film resistivity ρw
The wet film resistance (3.3) is multiplied by the electrode area relative to the distance between the electrodes
Note 1: Wet film resistivity is given by formula (3) :
![]()
Rw is wet film resistance;
A is the area of the electrode;
l is the length of the conductor.
The unit of wet film resistivity is ohm ·m (Ω·m).
3.7 Electrical conductivity γ
Reciprocal of resistivity (3.2)
Note 1: The conductivity is given by formula (4) :
![]()
The unit of conductivity is Siemens · m-1 (S · m-1).
[Source: ISO 15091:2019, 3.4]
Only the standard information section is public. To see the full content, you need to purchase the standard through the official channels.
