ISO 22553-7-2020, Farby i lakiery – powłoki elektroosadowe – Część 7: Odporność na mokrą warstwę
przedmowa
ISO (Międzynarodowa Organizacja Normalizacyjna) to globalna federacja krajowych organów normalizacyjnych (Organy członkowskie ISO). Opracowywanie norm międzynarodowych odbywa się zwykle za pośrednictwem komitetów technicznych ISO. Each member group interested in a subject on which a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on the Committee. International, governmental and non-governmental organizations in liaison with ISO are also involved in this work. ISO ściśle współpracuje z Międzynarodową Komisją Elektrotechniczną (IEC) we wszystkich kwestiach normalizacji elektrycznej.
Część 1 dyrektywy ISO/IEC opisuje procedury stosowane przy opracowywaniu tego dokumentu i dalszej konserwacji. W szczególności, note the different approval standards required for different types of ISO documents. This document has been drafted in accordance with the editorial rules in Part 2 dyrektywy ISO/IEC (zobacz iso.org/directives).
Należy pamiętać, że niektóre elementy tego dokumentu mogą być przedmiotem praw patentowych. ISO nie jest odpowiedzialna za identyfikację któregokolwiek lub wszystkich takich patentów. Details of any patent rights identified during the documentation development process will be included in the introduction and/or list of ISO patent claims received (zobacz iso.org/patents).
Any trade names used in this document are information provided for the convenience of the user and do not constitute an endorsement.
Explanations of the relevant standards of voluntary, ISO specific terms related to conformity assessment and the expression of meaning, and the ISO in the technical barriers to trade (Do ustalenia) przestrzegać zasad Światowej Organizacji Handlu (WTO) Informacja, please refer to the iso.org/iso/foreword.html.
This document has been prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 35, Farby i lakiery, Podkomisja SC 9, Wspólne metody badań farb i lakierów.
Lista wszystkich części w ISO 22553 można znaleźć na stronie internetowej ISO.
Any feedback or questions on this document should be referred to the user’s national standards body. A complete list of these institutions can be found at iso.org/members.html.
ISO 22553-7-2020, Farby i lakiery – powłoki elektroosadowe – Część 7: Odporność na mokrą warstwę
wprowadzić
Wet film resistivity provides information about the deposition behavior of electrodeposited coatings, to jest, information about film thickness and film thickness variation, homogeneous plating capacity, and possibly deposition properties under specific conditions.
1 Szereg zastosowań
This document specifies a method for determining the resistivity of wet films of electrodeposited coatings (e-coat) for the automotive industry and other general industrial applications (np. cooling units, consumer products, grzejniki, lotniczy, rolnictwo).
2 Normative reference files
When the following documents are referenced in the context, część lub całość stanowią wymagania niniejszego dokumentu. Dla przestarzałych odniesień, obowiązują wersje zawierające wyłącznie cytaty. Za niedatowane cytaty, the most recent version of the referenced document (including any amendments) ma zastosowanie.
ISO 1514, Farby i lakiery — Standard plates for testing
ISO 4618, Farby i lakiery – warunki i definicje
ISO 22553-1, Farby i lakiery – powłoki elektroosadzane – Część 1: Słownictwo
ISO 23321, Rozpuszczalniki do farb i lakierów – softening water for industrial applications – Specyfikacja i metody badań
3 Warunki i definicje
Na potrzeby niniejszego dokumentu, terminy i definicje podane w ISO 4618, ISO 22553-1 i poniżej obowiązują.
3.1 Resistance R
The ratio of the potential difference along a conductor to the current through it
Notatka wpisowa 1: Resistance is given by Ohm’s law as shown in formula (1) :
![]()
u is the potential difference;
I is current.
The unit of resistance is ohm (Ω), given by the following formula:
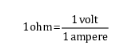
Resistance depends on the material, size (length and cross section) and temperature of the conductor.
[Źródło: ISO 15091:2019, 3.1]
3.2 Resistivity ρ
Cross-sectional area The resistance per unit length of a material
Pozycja Uwaga 1: Resistivity is given by formula (2) :
![]()
A is the cross-sectional area of the conductor;
I is the length of the conductor.
Resistivity is measured in ohms · meters (Ω·m).
[Źródło: ISO 15091:2019, 3.2]
3.3 Wet film resistance Rw
Measure the total resistance (3.1) of electrodeposited coatings, including substrates, pretreatments, and other coatings
Notatka 1: When measuring resistance, technical measurement conditions also have an effect, np. membrane, measuring electrode.
Notatka 2 The unit of wet film resistance is ohm (Ω).
3.4 Dynamic wet film resistance
![]()
The measured total resistance (3.1) of the electrodeposited coatings (including substrates, pretreatments, and other coatings) is a function of deposition time
Notatka 1 The unit of wet film resistance (3.3) is ohm (Ω).
3.5 Electrostatic wet film resistance
![]()
Measure the total resistance (3.1) of the electrodeposited coatings, including substrates, pretreatments and other coatings read out at the end of deposition time
Notatka 1 The unit of wet film resistance (3.3) is ohm (Ω).
3.6 Wet film resistivity ρw
The wet film resistance (3.3) is multiplied by the electrode area relative to the distance between the electrodes
Notatka 1: Wet film resistivity is given by formula (3) :
![]()
Rw is wet film resistance;
A is the area of the electrode;
l is the length of the conductor.
The unit of wet film resistivity is ohm ·m (Ω·m).
3.7 Electrical conductivity γ
Reciprocal of resistivity (3.2)
Notatka 1: The conductivity is given by formula (4) :
![]()
The unit of conductivity is Siemens · m-1 (S · m-1).
[Źródło: ISO 15091:2019, 3.4]
Tylko standardowa sekcja informacyjna jest publiczna. Aby zobaczyć pełną treść, musisz kupić standard za pośrednictwem oficjalnych kanałów.
